Insulin Resistance Unmasked: Breaking Free from the Silent Health Crisis
Development of Insulin Resistance
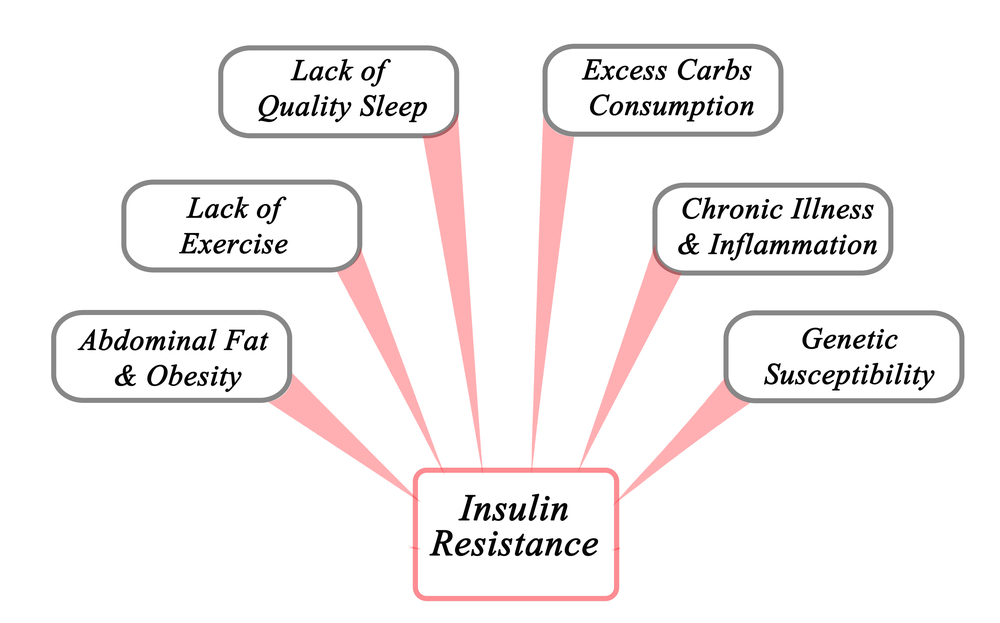
Insulin resistance typically develops gradually and is influenced by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to the development of insulin resistance. Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to efficiently use glucose for energy.

Poor Diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugary beverages, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates can contribute to insulin resistance. These foods lead to elevated blood sugar levels and increased demands on insulin production over time.
Obesity: Excess body weight, especially abdominal obesity, plays a significant role in the development of insulin resistance. Adipose tissue (fat cells) releases inflammatory substances that interfere with insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance.

Genetics: Certain genetic factors can predispose individuals to insulin resistance. A family history of type 2 diabetes or metabolic disorders can increase the likelihood of developing insulin resistance.
Prevention of Insulin Resistance
While some risk factors for insulin resistance, such as genetics, are beyond our control, there are several preventive measures that can be taken to reduce the risk or delay its onset:
Adopt a Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Minimize consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-calorie snacks. This can help regulate blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy body weight.

Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Incorporate regular exercise into your routine. Aim for a combination of aerobic activities (such as walking, jogging, or cycling) and strength training exercises. Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, helps with weight management, and reduces the risk of insulin resistance.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight is crucial for preventing insulin resistance. If you are overweight, even modest weight loss can have significant benefits for insulin sensitivity.
Avoid Sedentary Behavior: Reduce sedentary behavior by incorporating more movement throughout your day. Take breaks from sitting, make sure to stand up at least hourly, stretch, and move around regularly.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to insulin resistance. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, or seeking support from friends and family.

Get Regular Check-ups: Regular health check-ups can help monitor your blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, and other important markers of metabolic health. Detecting insulin resistance early allows for timely interventions.
Remember, prevention is key when it comes to insulin resistance. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a healthy weight, and being proactive about your overall well-being, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing insulin resistance and its associated consequences.
For more information and personalized advice, it is always best to consult with our clinic as we can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific health needs and circumstances. Give us a call today.

Here are some reputable websites where people can learn more about insulin resistance:
- American Diabetes Association (ADA): The ADA provides comprehensive information on insulin resistance, its relationship to diabetes, and tips for prevention. Visit their website at www.diabetes.org.
- Mayo Clinic: Mayo Clinic offers an in-depth overview of insulin resistance, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. They also provide practical advice on lifestyle modifications to prevent and manage insulin resistance. Explore their resources at www.mayoclinic.org.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): NIDDK, part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health, offers educational resources on insulin resistance, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes. Their website, www.niddk.nih.gov, includes information on research, prevention, and management strategies.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC provides valuable insights on insulin resistance, its risk factors, and preventive measures. Their website, www.cdc.gov, offers resources to help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
- Hormone Health Network: The Hormone Health Network, affiliated with the Endocrine Society, provides comprehensive information on hormonal disorders, including insulin resistance and its impact on hormonal balance. Visit www.hormone.org for reliable information and resources.