Prediabetes (borderline diabetes) explained as simply as possible…
Prediabetes is a condition that describes a person who has several abnormal glucose blood tests suggesting they have borderline diabetes. It may also be called “impaired glucose tolerance” or “metabolic syndrome.” People with Prediabetes are very likely to progress to developing diabetes in the coming few years. More importantly, people with Prediabetes are the most likely to recover and return to normal by making a few important changes.
Prediabetes (borderline diabetes) explained in a little more detail…
Prediabetes turns into Type 2 diabetes, and it is rapidly becoming one of the most common long-term diseases in the world. The problem causing an elevation in the blood glucose levels occurs when there is a change in the insulin receptor's shape. In the normal situation, the body produces a small chemical called insulin (key) whose purpose is to bind to a receptor (lock) on the surface of fat and muscle cells, opening a channel to allow glucose to enter those cells. In type 2 diabetes, the shape of this receptor changes mostly due to weight gain around the stomach.
What is metabolic syndrome?
Metabolic syndrome, sometimes called syndrome X, is a collection of disorders, including high blood pressure, insulin resistance, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excess fat around the waist. People with metabolic syndrome are twice as likely to have a heart attack and stroke and five times more likely to develop Type 2 Diabetes than people without metabolic syndrome.
Over the past three decades, the prevalence of Prediabetes (metabolic syndrome) has increased. More and more young people are showing signs of Prediabetes than ever before. The incidence of Prediabetes often parallels the incidence of Type 2 Diabetes and obesity. What’s scary is that a quarter of these adults don’t even realize that they have diabetes.
HAVING A FAMILY HISTORY OF DIABETES RAISES YOUR RISK OF PREDIABETES
Who is at risk of Prediabetes?
Risk factors can be divided into non-modifiable risk factors and modifiable risk factors. Non-modifiable risk factors are those that can’t be changed by you, for example, your genetics. Modifiable risk factors can be changed, for example making changes to how frequently you exercise.

Non-modifiable risk factors in Prediabetes?
Diabetes is much more common in people from certain ethnic backgrounds like Indian, Middle Eastern, South-East Asian, and Indigenous populations. In these groups, rates of diabetes can approach 30% of the adult population. In Caucasian populations, the rates are more typically 10% of the adult population.
The non-modifiable risk factors which increase your chance of developing Prediabetes include:
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Being older (over 55 years of age) – the risk increases as we age
- Ethnic background, including Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders, Pacific Islanders, Asian and South-East Asian, African Americans, Native Hawaiians, and Hispanics/Latinos
Being aware of the non-modifiable risk factors is extremely important. For people who have a family history of Type 2 Diabetes, you need to be more alert and start taking action early to prevent or delay developing Type 2 Diabetes.
Modifiable risk factors in Prediabetes
The modifiable risk factors which increase your chance of developing Prediabetes include:
- Being overweight, obese, or morbidly obese – particularly extra weight around the waist
- Being physically inactive, long hours of sitting.
- Eating a poor diet (one that is high in fat, salt, and sugar)
- High blood pressure

What are the symptoms of Prediabetes or borderline diabetes?
The most common symptom of Prediabetes is feeling nothing at all. Yep, nothing. That’s part of the problem. A person with undiagnosed Prediabetes feels ok, but the damage is already occurring. Many people experience tiredness and fatigue, which is really noticed when you start to get sugar levels under control.
In Type 2 Diabetes, the general symptoms include:
- Fatigue and irritability
- Excessive thirst, frequent urination, and dehydration
- Ongoing hunger
- Yeast and bacterial infections
- Dry and itchy skin
- Cuts and wounds that don’t heal quickly
- Pain and numbness in your feet or legs
- Blurred vision
- Changes in weight
PREDIABETES RAISES THE RISK OF HAVING LOW TESTOSTERONE IN MEN
Some symptoms of Diabetes can vary between men and women. Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in men are often related to sexual health and function. The symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes in women also often relate to sexual health and function.
How is Prediabetes diagnosed?
Most people diagnosed with Prediabetes are picked up by chance based on a high blood glucose reading noticed during routine blood testing. It is not the best way to test for Diabetes, so more formal tests should be asked for. This is typically a glucose tolerance test, or another test called an HbA1c. A glucose tolerance test involves a fasting blood test, 75g of glucose as a sugary drink, followed by another blood sugar test taken 2 hours later. Prediabetes is diagnosed when the sugar is too high to be normal and not high enough to have Diabetes.
Diagnosing Diabetes should not rely solely on using a Hb A1c test. In our office, we have an onsite lab that is able to do blood draws, making it easy for you to be tested.
What are the diagnostic criteria for Prediabetes?
People with Prediabetes can either have…
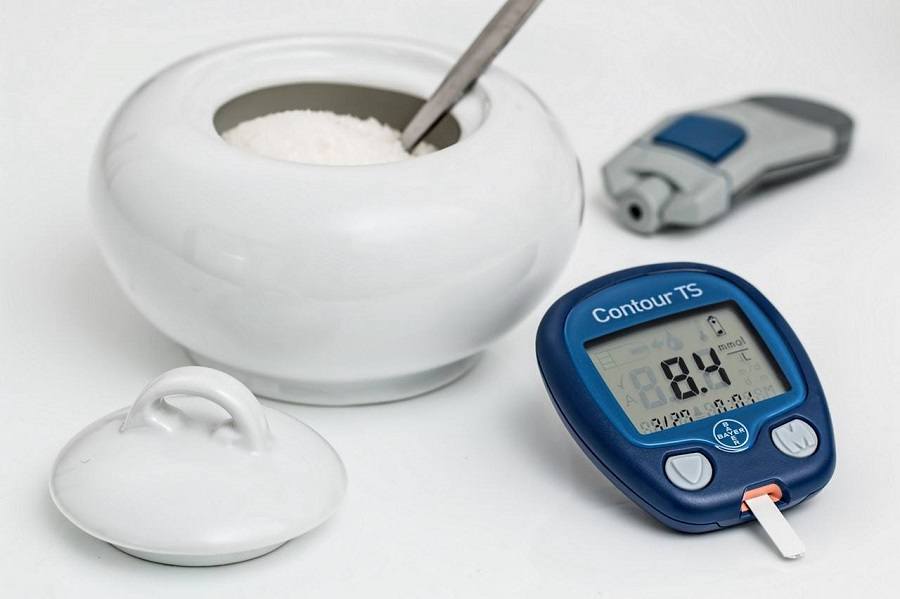
A) High fasting sugar levels

B) High post-meal sugar levels

C) Both high fasting and post-meal sugar levels
PEOPLE WITH PREDIABETES ARE AT HUGE RISK OF DEVELOPING DIABETES
Does Prediabetes develop and progress into Type 2 Diabetes?
Unfortunately, if left untreated, 37% of people with Prediabetes will go on to develop Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus within 4 years.
How often should I be tested for type 2 Diabetes?
If you have been diagnosed with Prediabetes, you should be tested every 12 months for Type 2 Diabetes.
Is Prediabetes dangerous, and can it cause problems?
Prediabetes is a very serious condition. People with Prediabetes are at an increased risk of heart attacks as well as strokes, and some Cancers. Even though blood glucose levels are only mildly elevated, people can still have abnormalities with their cholesterol levels and high blood pressure (Hypertension). These factors also contribute to the high rates of heart disease seen in people with Type 2 Diabetes.
People with Prediabetes who have ongoing high blood glucose levels are at an increased risk of having poor health outcomes than people who do not have Prediabetes.
Important facts that you need to know that relate to people with Diabetes:
- People with Diabetes are up to four times more likely to suffer heart attacks or strokes.
- Diabetes is the leading cause of vision loss globally. It is the fifth most common cause of preventable blindness as well as moderate to severe visual impairment.
- Kidney failure is three times more common in people with Diabetes.
- Amputations are 15 times more common in people with Diabetes.
- More than 30 percent of people with Diabetes experience depression, anxiety, and distress
- Early diagnosis, optimal treatment, and effective ongoing support and management reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications dramatically.
What are the complications of Prediabetes?
If left untreated, Prediabetes can become Type 2 Diabetes. Type 2 Diabetes is associated with several complications affecting the blood vessels in our bodies. Complications in Type 2 Diabetes can be described as microvascular (small blood vessels) or macrovascular (large blood vessels) complications. Diabetes-related complications occur over time due to persistent high blood glucose levels, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels. These complications are serious and can be life-threatening.
Macrovascular complications – Problems with large blood vessels
Macrovascular disease affects the larger blood vessels in our body that supply blood to the heart, brain, and legs. Macrovascular complications include:
- Coronary artery disease can lead to a heart attack.
- A cerebrovascular disease that can lead to a stroke
Peripheral artery disease leads to pain deep in the leg muscles (calves, thigh, or buttocks pain during activity) and amputations.
Microvascular complications – Problems with small blood vessels
Like macrovascular disease, ongoing high blood glucose levels are an important risk factor for developing a microvascular disease in patients with Type 2 Diabetes.
Microvascular complications include:
- Retinopathy – Disease of the eye which can lead to blindness
- Neuropathy – Disease of the nerves which can lead to foot ulcers requiring amputation
- Nephropathy – Disease of the kidneys which leads to kidney failure and the need for dialysis
How can I prevent Prediabetes from progressing to Type 2 Diabetes?
There are changes you can make to improve your health and prevent Type 2 Diabetes. For people with Prediabetes, lifestyle modification can lead to a 40-70% reduction in the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes.
You can prevent type 2 diabetes through:
- Being at a healthy weight
- Setting realistic goals
- Getting support from your family and friends
- Make slight changes as part of your everyday routine.
- Knowledge – Diabetes education is crucial
- Eating well is understanding how carbohydrates, good fats/bad fats, salt, and SUGAR work for your body and to prevent tipping over into Type 2 Diabetes.
There is evidence that quitting smoking will help to reduce your risk of developing Diabetes. Similarly, we all know quitting smoking lowers your risk of having a stroke or heart attack.
Making these changes can also reduce your risk of developing Diabetes comorbidities, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
If you have Prediabetes, our ReSet Metabolic Weight Loss program can be tailored to your needs. It will provide you with the best advice, support, and education to help you get back on track and prevent Prediabetes from becoming Type 2 Diabetes.
What should a person with Prediabetes do?
The first thing to do once diagnosed with Prediabetes is to improve your knowledge. This is a disease that is not solved in the doctor's office but rather by making the right choices most of the time. Our understanding of Diabetes and how to control it has improved dramatically over the last few years. Yet, most people with Diabetes have not been given the tools or understanding to be involved in managing their condition. We help you manage YOUR condition in a way that works best for you – this is not a cookie-cutter approach to care, it's care made for you.
You will improve your knowledge by joining our ReSet Metabolic Weight Loss program. The program will provide you with all of the information and support you need while motivating you to stay on track, and make successful healthy choices around food, exercise, water intake, and sleep patterns..

What should I do next?
Call us and get scheduled to come in! If you experience any symptoms of Prediabetes or risk factors for developing Prediabetes, it is important to get tested as soon as possible. Some people are at higher risk and need regular testing. We have on-site daily testing available.
If you are 45 years or older or have other risk factors for Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes, you will require more frequent testing. By diagnosing and treating Prediabetes early, it means you will decrease the risk of developing or delaying any further health complications of Prediabetes, for example, nerve damage, blindness, and heart disease. It is important to know that diagnosing Prediabetes should not rely solely on using a Hb A1c test.
Once we learn what your diagnosis is or have Prediabetes, the next most important step is to become educated. By joining the ReSet Metabolic Weight Loss program, you will receive the help and education you need to learn how best to manage your condition. For example, you will learn how best to monitor your diet and create an exercise program that works with your lifestyle. The ReSet program is personalized and tailored, giving you more of the content you need when you want it.

