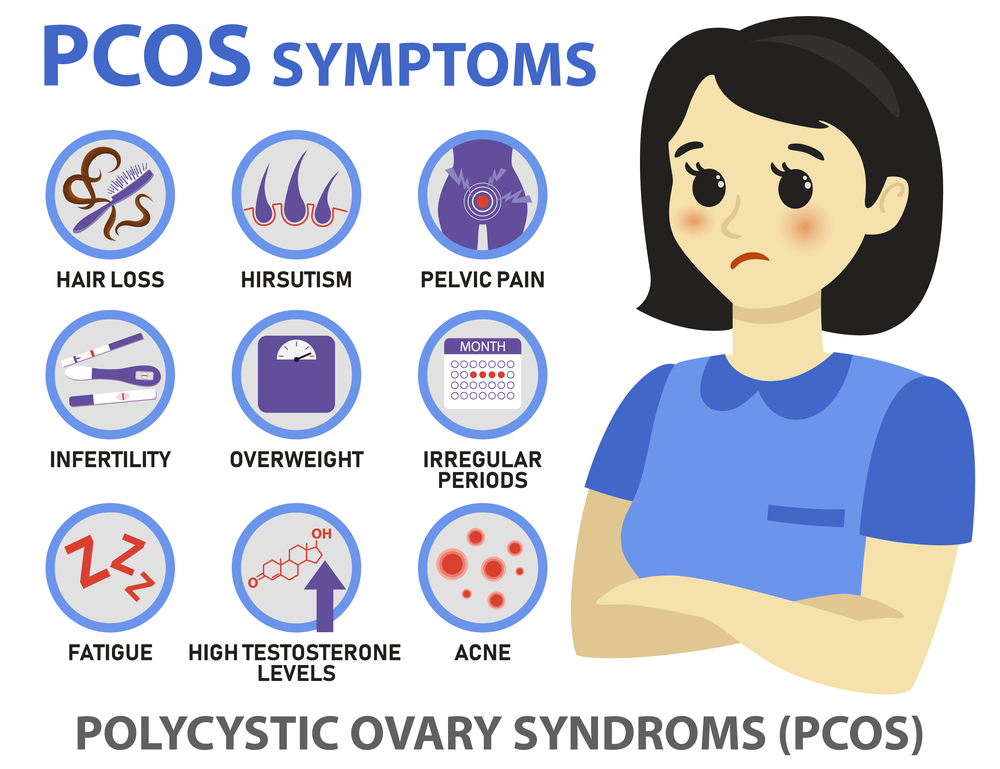
Q: What Differentiates PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) From Other Diagnoses?
A:
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by a combination of symptoms, and several factors differentiate PCOS from other diagnoses:
Common differences include menstrual irregularities, hyperandrogenism, ovarian cysts, insulin resistance, and metabolic abnormalities. Let’s review each in a bit more detail.
Menstrual Irregularities
PCOS often leads to irregular or absent menstrual periods. Women with PCOS may experience infrequent, prolonged, or heavy menstrual bleeding. In contrast, other conditions may have different patterns of menstrual irregularities or may not affect menstruation at all.
Hyperandrogenism

PCOS is associated with higher levels of androgens (male hormones) in the body. This can lead to symptoms such as excess facial or body hair (hirsutism), acne, and male-pattern baldness (alopecia). While other conditions can also cause these symptoms, the combination of hyperandrogenism and menstrual irregularities is a hallmark of PCOS.
Ovarian Cysts
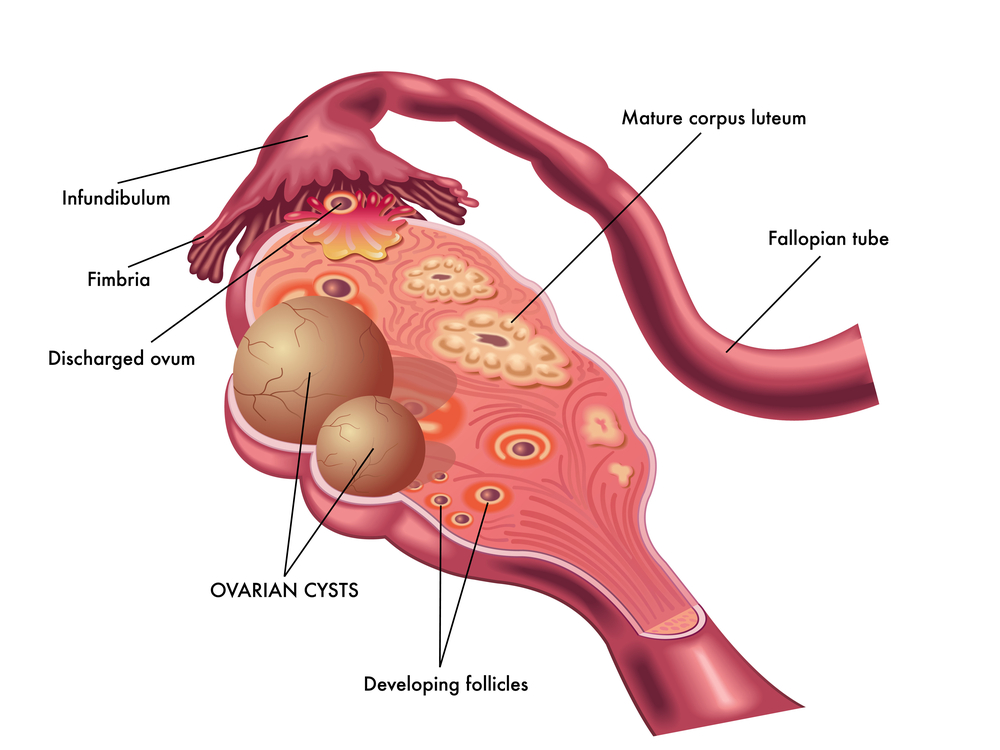
The presence of ovarian cysts is common in PCOS, but it is not a diagnostic requirement. These cysts are typically small and often do not cause any symptoms. Other conditions, such as functional ovarian cysts, may also produce ovarian cysts, but they are usually temporary and resolve on their own.
Insulin Resistance
Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, meaning their cells are less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Other conditions may also involve insulin resistance, but it is often a prominent feature of PCOS.
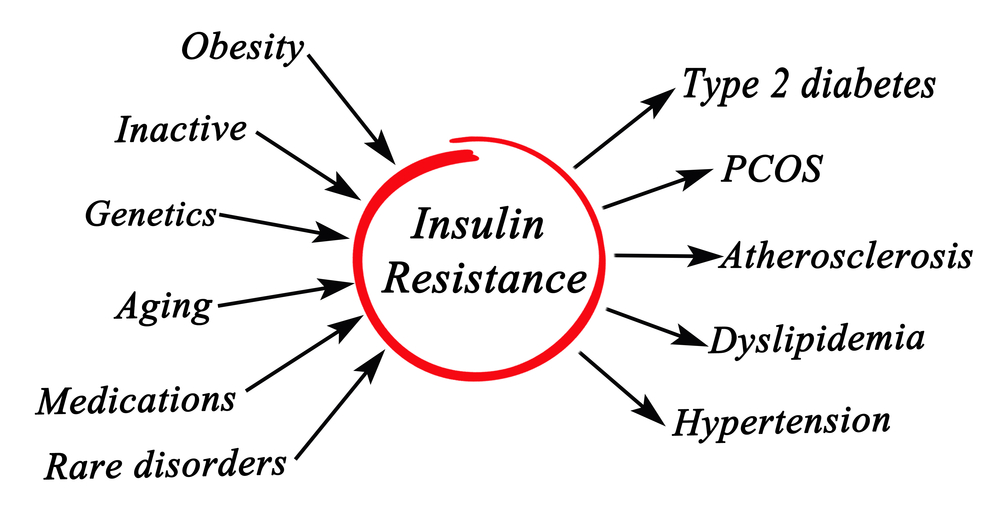
Metabolic Abnormalities
PCOS is associated with metabolic abnormalities such as obesity, dyslipidemia (abnormal cholesterol levels), and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. These metabolic disturbances may be more pronounced in women with PCOS compared to other conditions.
It’s important to note that PCOS is a complex condition, and the diagnosis is typically made based on a combination of symptoms, physical examination findings, and laboratory tests. A healthcare professional should evaluate and differentiate PCOS from other possible diagnoses to provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.