Your Thyroid – Things you should know
The thyroid gland is vital to the human body’s endocrine system. The endocrine system is an incredibly complex and important part of the human body. It regulates hormones that control important processes like growth and metabolism. The Endocrine system is comprised of several organs including the pancreas, brain, thyroid gland, testicles in men, and ovaries in women.
These organs release hormones into the bloodstream. This helps control various processes throughout the body. Within your body, several glands work together to control one another. As a result, a disease might impact a single gland or numerous glands in the body. Let’s explore more about your Thyroid and why it is so important in your body.
1. Location and Structure
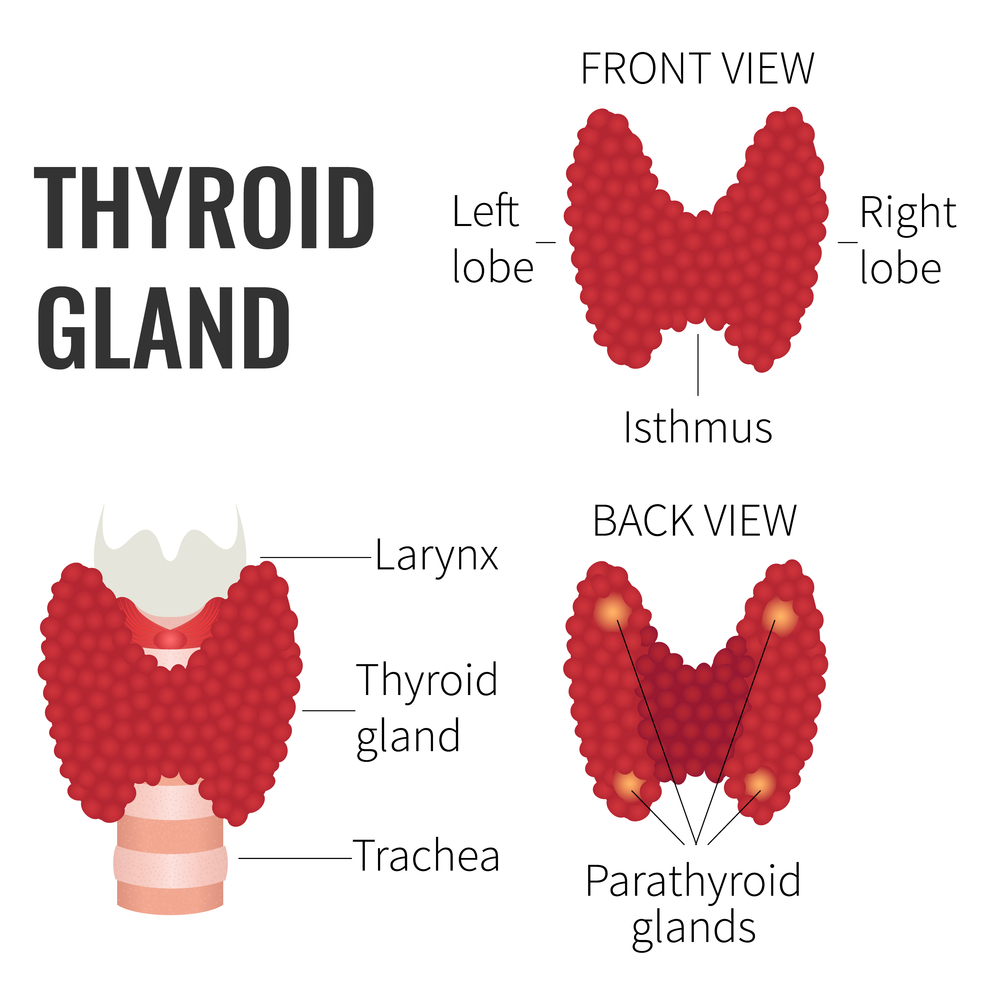
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below Adam’s apple. It is made of two lobes that are connected by a narrow band of tissue called the isthmus.
The gland is comprised of many small spherical structures called follicles. They are surrounded by thyroid cells and filled with a gel-like substance called colloid.
2. Hormone Production
The thyroid gland produces two main hormones, Thyroxin (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3). They are essential for regulating metabolism, growth, and development throughout the body. These hormones are made up of iodine atoms. These atoms are obtained from the diet. The thyroid gland uses iodine to synthesize T4 and T3. They are then released into the bloodstream.
- Regulation of Hormone Production
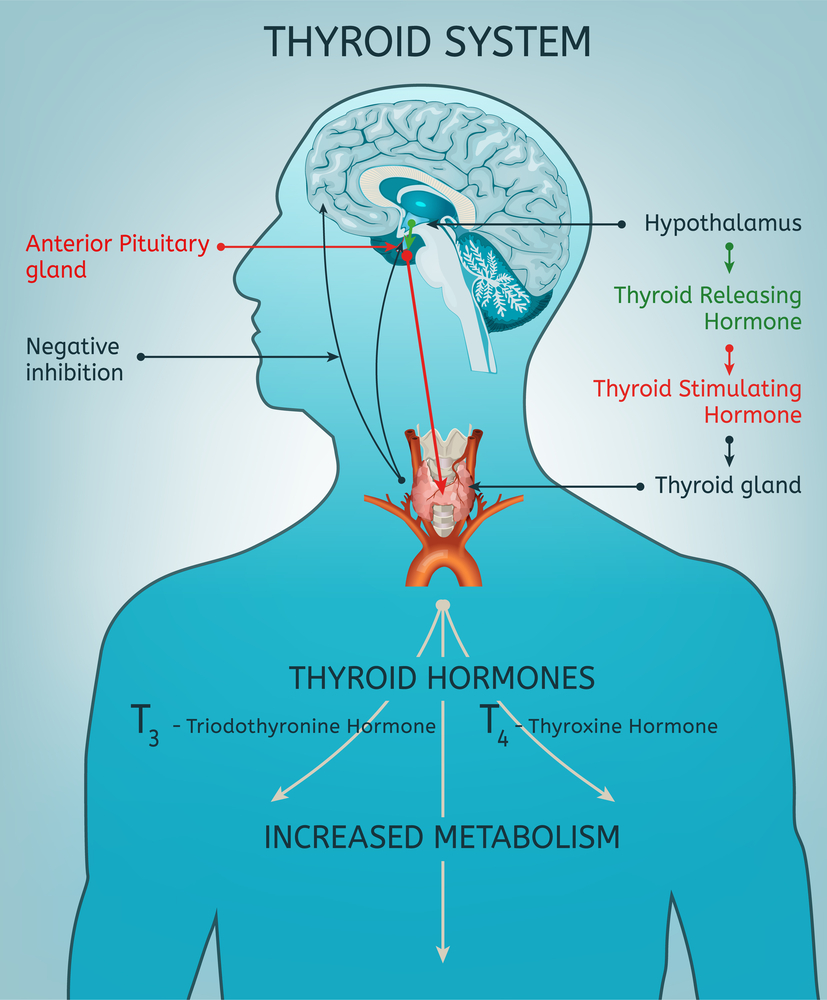
The production of thyroid hormones is regulated by a complex feedback loop. This involves the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland.
The hypothalamus produces a hormone called thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). It signals the pituitary gland to release Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH).
TSH then stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release T4 and T3. When the levels of T4 and T3 in the bloodstream are high enough, they signal the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to slow down the production of TRH and TSH, respectively.
- Role in Metabolism
Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism. Metabolism is the process by which the body converts food into energy. In addition, thyroid hormones help to regulate the levels of other hormones in the body, including insulin and cortisol.
3. Growth and Development
Thyroid hormones are important for growth and development, particularly in children and adolescents. They help to stimulate the growth and development of bones and muscles, brain, and nervous system. Thyroid hormones are also necessary for proper sexual development and reproductive function.
4. Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders are very common, affecting an estimated 20 million Americans. The most common thyroid disorders are hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid).
These conditions can have a wide range of symptoms and can be caused by various factors, including autoimmune disease, iodine deficiency, and certain medications. Other thyroid disorders include thyroid nodules, goiter (an enlarged thyroid gland), and thyroid cancer.
- Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones. This can cause a range of symptoms including fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and depression. It is typically diagnosed through a blood test to measure the levels of thyroid hormones and TSH in the body. Hypothyroidism is typically treated with thyroid hormone replacement therapy. It involves taking a synthetic form of thyroid hormone orally.

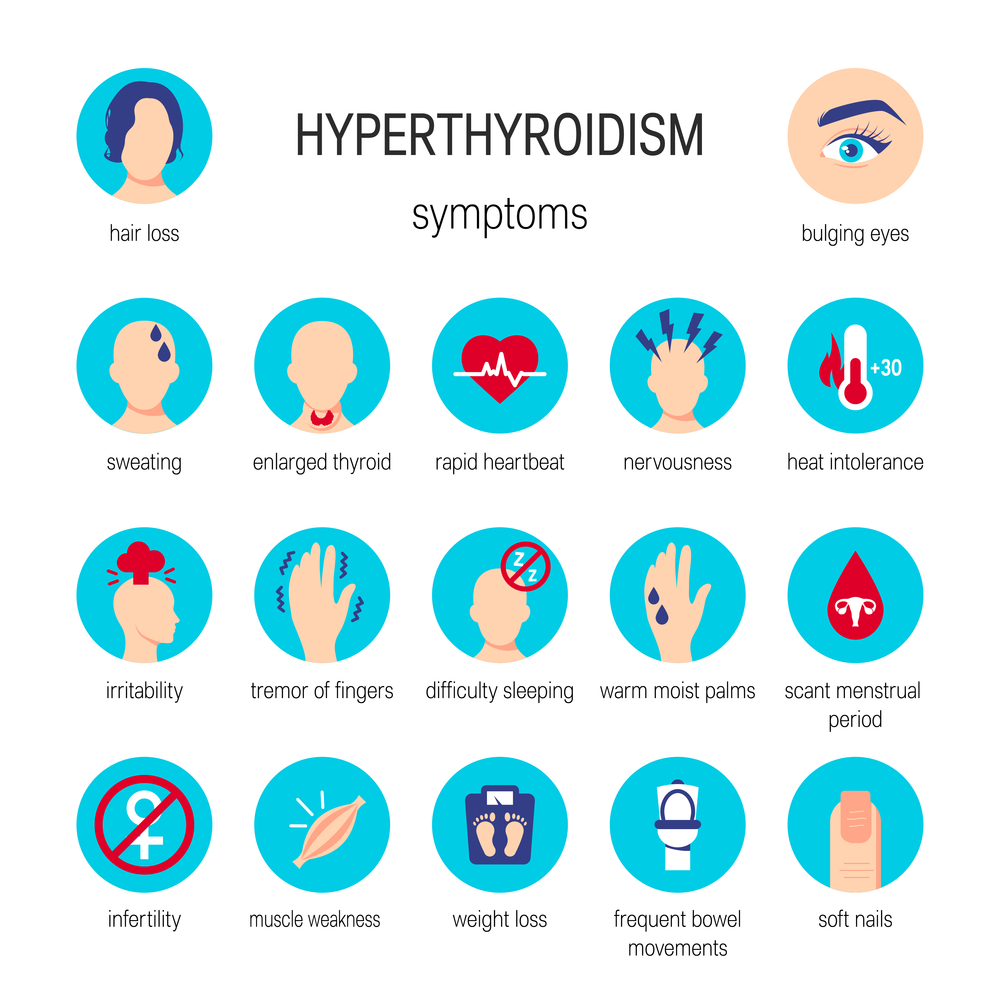
- Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. This can cause symptoms such as weight loss, anxiety, increased heart rate, and difficulty sleeping. It is also typically diagnosed through a blood test to measure the levels of thyroid hormones and TSH in the body. Hyperthyroidism is mainly treated with medications that reduce the production of thyroid hormones or with radioactive iodine therapy, which involves taking a radioactive form of iodine orally.
- Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is a rare but serious form of cancer. It begins in the thyroid gland. It can occur in people of any age but is most common in women and people over the age of 60. The most common type of thyroid cancer is papillary thyroid cancer. This accounts for about 80% of cases. Other types of thyroid cancer include follicular thyroid cancer, medullary thyroid cancer, and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Treatment for thyroid cancer usually involves surgery to remove the thyroid gland, followed by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy.
- Prevention and Management
There are several ways to help prevent thyroid disorders and manage symptoms if they occur. Eating a healthy diet that includes iodine-rich foods such as seafood, dairy products, and eggs can help ensure that the thyroid gland has enough iodine to produce hormones.
Regular exercise and stress management techniques such as meditation or yoga can also help support thyroid function. If you have a thyroid disorder, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage your symptoms and monitor your thyroid hormone levels.
In some cases, lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery may be necessary to manage thyroid disorders. We can help determine which is the best for you.

Learning about the function of the thyroid gland is essential for staying healthy. Thyroid hormone and other hormone testing might provide light on your overall health.
Our clinic offers a range of services that can help you better understand your body’s health through endocrinology testing, diagnosis, and treatment. We even have an on-site lab to be able to do testing easily for our patients. To learn more about Thyroid Issues and how our clinic can help, click here.