Neuropathy 101: Navigating Nerves for Diabetic and Thyroid Patients
Neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage, is a significant concern for individuals with diabetes and thyroid disorders.
Both of these medical conditions can increase the risk of developing neuropathy and can have a substantial impact on an individual’s quality of life. In this blog, we will explore the common issues of neuropathy that affect diabetic and thyroid patients, as well as discuss management strategies and potential treatments to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Understanding Neuropathy
Neuropathy refers to a condition that affects the peripheral nervous system, responsible for transmitting signals between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body. When nerves are damaged, individuals may experience a range of symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling sensations, muscle weakness, and coordination problems.
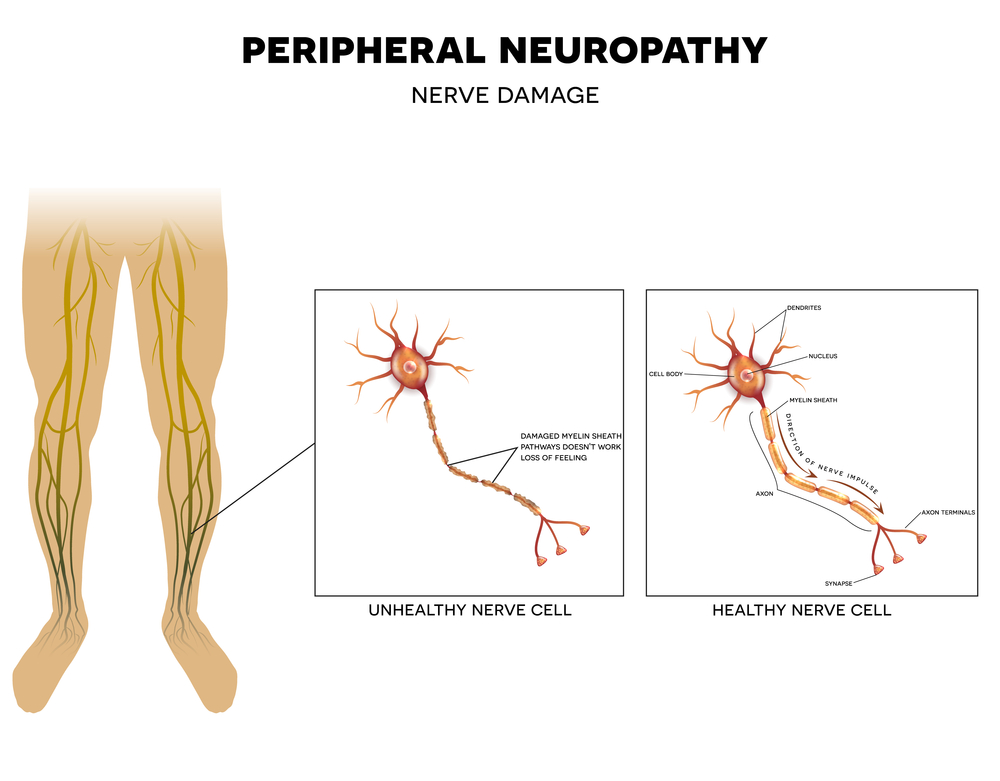
Neuropathy in Diabetic Patients
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Prolonged periods of high blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to diabetic neuropathy. The most common types of diabetic neuropathy include peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, proximal neuropathy, and focal neuropathy.
Peripheral neuropathy affects the nerves in the extremities, such as the hands and feet, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, and pain. Autonomic neuropathy affects the nerves that control automatic bodily functions, resulting in issues like digestive problems, urinary incontinence, and cardiovascular abnormalities.
Proximal neuropathy primarily affects the hips, thighs, and buttocks, causing muscle weakness and pain. Focal neuropathy is characterized by damage to specific nerves, resulting in sudden weakness or pain in a specific area.
Neuropathy in Thyroid Patients
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, and when it malfunctions, it can lead to thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Both of these conditions have been associated with an increased risk of developing neuropathy.
Hypothyroidism, characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, can cause nerve damage due to reduced metabolism and circulation. Symptoms of neuropathy in hypothyroidism may include muscle cramps, muscle weakness, and slowed reflexes.
Hyperthyroidism, on the other hand, occurs when the thyroid gland is overactive, resulting in an increased metabolic rate. Neuropathy in hyperthyroidism can manifest as muscle weakness, tremors, and fine motor coordination difficulties.
Management Strategies and Treatments
Blood Sugar Control
For diabetic patients, maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial in preventing and managing neuropathy. Consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels, adherence to a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication as prescribed by a healthcare professional can help achieve stable blood sugar control.
Thyroid Medication
Patients with thyroid disorders should follow their doctor’s recommendations regarding thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Properly managing the thyroid condition can aid in reducing the risk and severity of neuropathy symptoms.
Medications for Symptom Relief
Depending on the type and severity of neuropathy symptoms, doctors may prescribe medications to alleviate pain, such as analgesics, anticonvulsants, or antidepressants. These medications work by targeting the specific symptoms associated with neuropathy, providing relief and improving quality of life.
Physical Therapy
Engaging in physical therapy exercises and activities can help improve muscle strength, balance, and coordination. Physical therapists can design tailored programs to address individual needs and minimize the impact of neuropathy on daily functioning.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief from neuropathy symptoms through alternative therapies like acupuncture, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), and herbal remedies. While the effectiveness of these approaches may vary, it’s important to consult with your provider at DETS to review what options are best for you.
Neuropathy is a common issue for individuals with diabetes and thyroid disorders. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms of neuropathy in these conditions is crucial for effective management.
By prioritizing blood sugar control, adhering to thyroid medication, and exploring various treatment options, individuals can find relief from neuropathy symptoms and improve their overall well-being. Consulting with healthcare professionals is essential to develop a personalized approach to managing neuropathy, ensuring the best possible outcomes for diabetic and thyroid patients.